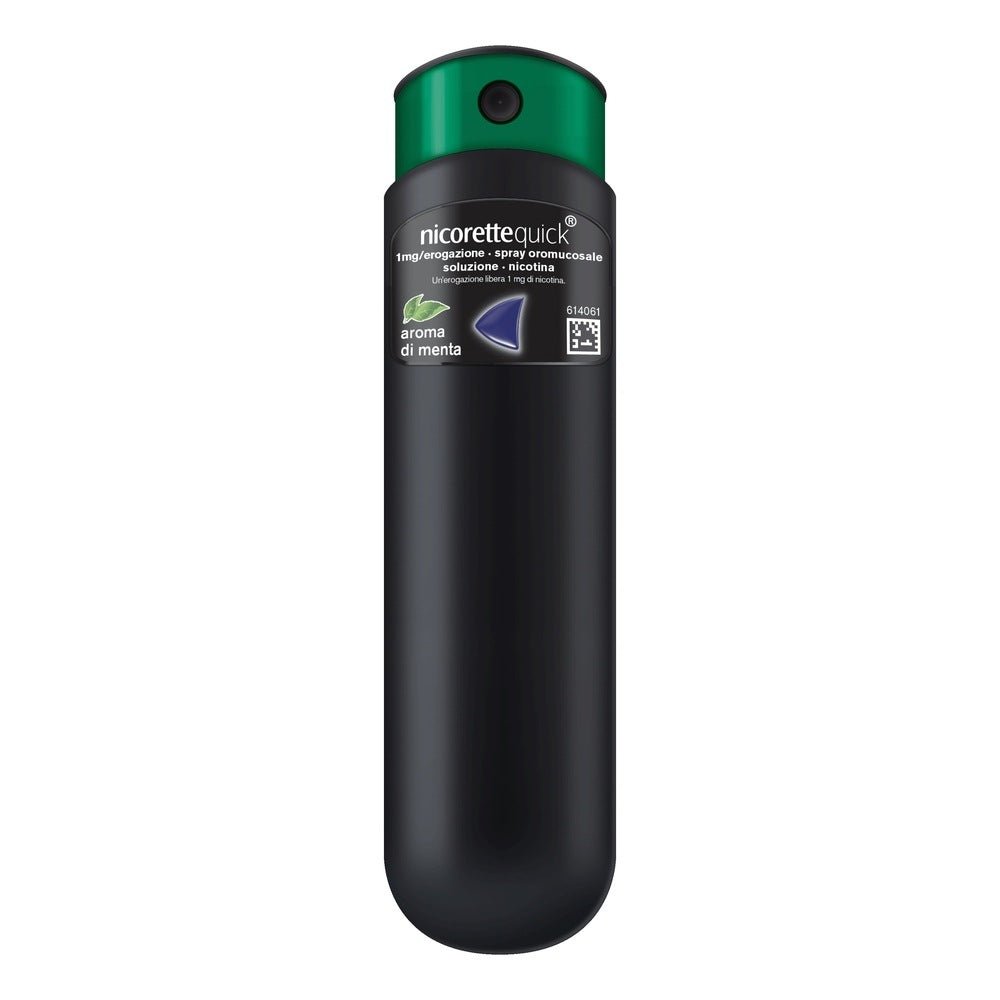
NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses is a medical device designed to support adults in the treatment of tobacco dependence . Each spray delivers 1mg of nicotine in 0.07ml of solution, providing rapid relief from nicotine withdrawal symptoms, including the desire to smoke. This oromucosal spray is ideal for those who want to gradually reduce their smoking habit or for those who are ready to quit completely. The formulation includes ethanol , propylene glycol and butylated hydroxytoluene , among other excipients, to ensure effective delivery of nicotine. With a total of 150 doses , NicoretteQuick represents a practical and discreet solution for managing nicotine cravings at any time of the day.
ACTIVE INGREDIENTS
Active ingredients in NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - What is the active ingredient in NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses?
One free spray 1 mg nicotine in 0.07 ml solution. 1 ml solution contains 13.6 mg nicotine. Excipients with known effect : Ethanol 7.1 mg/spray; Propylene glycol 11 mg/spray; Butylated hydroxytoluene 363 ng/spray. For the full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
EXCIPIENTS
Composition of NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - What does NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses contain?
Propylene glycol (E1520), Anhydrous ethanol, Trometamol, Poloxamer 407, Glycerol (E422), Sodium hydrogen carbonate, Levomenthol, Mint flavour, Refreshing flavour, Sucralose, Acesulfame potassium, Butylated hydroxytoluene (E321), Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment), Purified water.
DIRECTIONS
Therapeutic indications NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - Why is NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses used? What is it used for?
Nicorettequick is used to treat tobacco dependence in adults by relieving nicotine withdrawal symptoms, including cravings during a smoking cessation attempt or to reduce smoking habits before stopping smoking completely. The ultimate goal is permanent cessation of tobacco use. The use of Nicorettequick should preferably be combined with a behavioral support program.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS
Contraindications NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - When should NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses not be used?
• Hypersensitivity to nicotine or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1. • Children under 18 years. • Subjects who have never smoked.
DOSAGE
Quantity and method of taking NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - How to take NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses?
Dosage Support and behavioural therapy usually increase the success rate. Adults and elderly Up to 4 sprays per hour may be used. Do not exceed 2 sprays of each strength and 64 sprays (4 sprays per hour over 16 hours) in any 24-hour period. Abrupt Stopping Smoking For smokers who want and are prepared to stop smoking immediately. People should stop smoking completely during treatment with Nicorettequick. The following chart shows the recommended timing of use for the oromucosal spray during full treatment (phase I) and during the reduction phases (phase II and phase III). Phase I: weeks 1 to 6 Use 1 or 2 sprays when you would have smoked a cigarette or if you feel the urge to smoke. If one spray does not control the urge to smoke within a few minutes, spray a second spray. If 2 sprays are needed, 2 consecutive sprays may be used in the future. Most smokers will need 1 or 2 sprays every 30 minutes to 1 hour. Phase II: Weeks 7 to 9 Begin reducing the number of sprays per day. By the end of Week 9, subjects should have HALVED the average number of sprays per day used in Phase I. Phase III: Weeks 10 to 12 Continue reducing the number of sprays per day so that by Week 12, subjects are using no more than 4 sprays per day. When subjects have reduced the number of sprays to 2 to 4 per day, use of the oromucosal spray should be stopped. Example: If an average smoker smokes 15 cigarettes per day, 1 to 2 sprays should be used at least 15 times throughout the day. To help them continue to quit smoking after Phase III, subjects may continue to use the oromucosal spray in situations where they are strongly tempted to smoke. A single spray may be used in situations where there is an urge to smoke, with a second spray if the first has not had any effect within a few minutes. At this stage, no more than four sprays should be used per day. Gradual cessation through progressive reduction in smoking. For smokers who are unwilling or unready to stop smoking abruptly. The oromucosal spray may be used between cigarettes in order to prolong smoke-free intervals and with the aim of reducing smoking as much as possible. The patient should be aware that inappropriate use of the spray may increase adverse effects. One cigarette should be replaced by one dose (1-2 sprays) and a quit attempt should be made as soon as the smoker feels ready and in any case no later than 12 weeks after starting treatment. If a reduction in cigarette consumption is not achieved after 6 weeks of treatment, a healthcare professional should be consulted. After smoking cessation, the number of sprays per day should be gradually reduced. When subjects have reduced dosing to 2-4 sprays per day, the oromucosal spray should be discontinued. Regular use of the oromucosal spray beyond 6 months is not recommended. Some ex-smokers may require longer treatment with the oromucosal spray to avoid resuming smoking. Residual oromucosal spray should be stored for use in the event of a sudden craving to smoke. Paediatric population Do not administer Nicorettequick to subjects under 18 years of age. There is no experience in treating adolescents under 18 years of age with Nicorettequick. Method of administration After preparation, aim the spray nozzle as close to the mouth as possible. Press the top of the dispenser firmly and release one spray into the mouth, avoiding the lips. Subjects should not inhale during actuation, to avoid spraying into the airways. For best results, do not swallow for a few seconds after actuation. Subjects should not consume food or drink at the same time as taking the oromucosal spray.
CONSERVATION
Storage NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - How should NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses be stored?
Do not store above 30 ° C
WARNINGS
Warnings NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - About NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses it is important to know that:
Nicorettequick should not be used by non-smokers. The benefits of stopping smoking outweigh any risks associated with the correct administration of nicotine replacement therapy (NRT). A benefit-risk assessment should be made by appropriate medical professionals for patients with the following conditions: • Cardiovascular disease: Dependent smokers who have recently had myocardial infarction, unstable or worsened angina including Prinzmetal's angina, serious cardiac arrhythmias or recent cerebrovascular accident and/or who have uncontrolled hypertension should be encouraged to stop smoking by non-pharmacological interventions (e.g. counselling). If these fail, the oromucosal spray may be considered but, as safety data in this patient group are limited, treatment should only be initiated under close medical supervision. • Diabetes mellitus. Patients with diabetes mellitus should be advised to monitor blood glucose levels more closely than usual when stopping smoking and starting NRT, as the reduction in catecholamine release induced by nicotine may affect carbohydrate metabolism. • Allergic reactions : predisposition to angioedema and urticaria. • Renal and hepatic impairment: use with caution in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment and/or severe renal impairment, as there may be a decrease in the clearance of nicotine or its metabolites, with the possibility of an increase in adverse effects. • Phaeochromocytoma and uncontrolled hyperthyroidism: use with caution in uncontrolled hyperthyroidism or phaeochromocytoma, as nicotine causes the release of catecholamines. • Gastrointestinal disease: nicotine may exacerbate symptoms in patients with esophagitis, gastric or peptic ulcers; NRT preparations should be used with caution in such conditions. Paediatric population Hazard in children : Doses of nicotine tolerated by smokers may cause serious toxicity in children, including fatal outcomes. Nicotine-containing products should not be left where they can be handled or ingested by children; see section 4.9 Overdose. Transmitted dependence: Transmitted dependence can occur, but is less harmful and easier to break than smoking dependence. Smoking cessation: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tobacco smoke induce the metabolism of drugs metabolised by CYP1A2 (and probably CYP1A1). When a smoker stops smoking, he or she may experience a slower metabolism, resulting in increased blood levels of these drugs. This is potentially more clinically relevant for products with a narrow therapeutic window, such as theophylline, tacrine, clozapine and ropinirole. With cessation of tobacco use, the plasma concentrations of other medicinal products that are partly metabolised by CYP1A2 (e.g. imipramine, olanzapine, clomipramine and fluvoxamine) may increase, although data to support this are limited and the possible clinical significance of this effect for these medicinal products is unknown. Limited data indicate that smoking may induce the metabolism of flecainide and pentazocine. Excipients: This medicinal product contains approximately 7 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per actuation, which is equivalent to 97 mg per mL. The amount per actuation is equivalent to less than 2 mL of beer or 1 mL of wine. The small amount of alcohol in this medicinal product will not have any significant effect. This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per actuation, i.e. essentially 'sodium-free'. This medicinal product contains 11 mg of propylene glycol per actuation, equivalent to 150 mg/mL. Due to the presence of butylated hydroxytoluene, Nicorettequick may cause localized skin reactions (e.g. contact dermatitis) or irritation to the eyes and mucous membranes. Care should be taken to avoid contact of the oromucosal spray with the eyes during administration.
INTERACTIONS
Interactions NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - Which medicines or foods can modify the effect of NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses?
No clinically significant interactions between nicotine replacement therapy and other drugs have yet been confirmed. However, nicotine may increase the haemodynamic effects of adenosine, i.e. increased blood pressure and heart rate, as well as increased pain response (angina-like chest pain) caused by adenosine administration (see section 4.4, Smoking cessation).
SIDE EFFECTS
Like all medicines, NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses can cause side effects - What are the side effects of NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses?
Nicotine Withdrawal Effects Regardless of the means used, a variety of symptoms are known to be associated with cessation of habitual tobacco use. These include emotional or cognitive effects such as dysphoria or depressed mood; insomnia; irritability, frustration or anger; anxiety; difficulty concentrating; and restlessness or impatience. Physical effects may also occur such as a decrease in heart rate; increased appetite or weight, dizziness or presyncopation, cough, constipation, gum bleeding or aphthous ulceration, or nasopharyngitis. Additionally, and of clinical importance, nicotine cravings may cause a profound urge to smoke. Nicorettequick may cause adverse reactions similar to those associated with nicotine taken in other ways and are primarily dose-dependent. In susceptible individuals, allergic reactions such as angioedema, urticaria or anaphylaxis may occur. Local adverse effects of administration are similar to those seen with other oral forms. In the first few days of treatment, irritation of the mouth and throat may occur; hiccups are also a particularly common effect. Habituation is normal with prolonged use. Daily data collection from study subjects demonstrated that the most common adverse events were reported with an onset in the first 2-3 weeks of use of the oromucosal spray, and then decreased. Adverse reactions observed with oromucosal nicotine formulations identified from clinical trials and during post-marketing experience are presented below. The frequency category was estimated from clinical trials for adverse reactions identified during post-marketing experience. Very common (≥1/10); common (≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000); very rare (<1/10,000); not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data).
| Classification by Systems and Organs | Reported Adverse Reactions |
| Immune system disorders | |
| Common | Hypersensitivity |
| Not known | Allergic reactions, including angioedema and anaphylaxis |
| Psychiatric disorders | |
| Uncommon | Anomalous dreams |
| Nervous system disorders | |
| Very common | Headache |
| Common | Dysgeusia, paresthesia |
| Eye pathologies | |
| Not known | Blurred vision, increased tear production |
| Heart disease | |
| Uncommon | Palpitations, tachycardia |
| Not known | Atrial fibrillation |
| Vascular pathologies | |
| Uncommon | Redness, hypertension |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders : | |
| Very common | Hiccups, throat irritation |
| Common | Cough |
| Uncommon | Bronchospasm, rhinorrhea, dysphonia, dyspnea, nasal congestion, oropharyngeal pain, sneezing, throat tightness |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | |
| Very Common | Nausea |
| Common | Abdominal pain, dry mouth, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, salivary hypersecretion, stomatitis, vomiting |
| Uncommon | Eructation, bleeding gums, glossitis, blisters and peeling of the oral mucosa, oral paresthesia |
| Rare | Dysphagia, oral hypoesthesia, retching |
| Not known | Dry throat, gastrointestinal disturbances, sore lips. |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | |
| Uncommon | Hyperhidrosis, pruritus, rash, urticaria |
| Not known | Erythema |
| Systemic disorders and conditions related to the administration site | |
| Common | Burning sensation, fatigue |
| Uncommon | Asthenia, chest discomfort and pain, malaise |
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions . Reporting suspected adverse reactions that occur after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the national reporting system at www,aifa.gov.it/content/segnalazioni-reazioni-avverse.
OVERDOSE
Overdose NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses - What are the risks of NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses in case of overdose?
Direct symptoms of nicotine overdose may occur in patients with a low pre-treatment nicotine intake or if nicotine is taken simultaneously from multiple sources. Symptoms of overdose coincide with those of acute nicotine poisoning and include nausea, vomiting, increased salivation, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, sweating, headache, dizziness, hearing disturbances and marked weakness. At high doses, these symptoms may be followed by hypotension, weak and irregular heartbeat, respiratory distress, fatigue, circulatory collapse and generalised convulsions. Paediatric population Doses of nicotine tolerated by adult smokers during treatment may cause severe poisoning symptoms, including fatal outcomes in children. Suspected nicotine poisoning in a child should be treated as a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention. Management of overdose: Nicotine administration should be stopped immediately and the patient treated symptomatically. If excessive amounts of nicotine are ingested, activated charcoal reduces the gastrointestinal absorption of nicotine. The minimum acute lethal oral dose of nicotine in humans is thought to be 40 to 60 mg.
PREGNANCY AND BREASTFEEDING
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses.
Women of Childbearing Age / Contraception in Men and Women The adverse effects of tobacco smoking on human conception and pregnancy are known, while the effects of nicotine-based therapeutic treatment are unknown. Therefore, since no specific recommendations regarding the need for female contraception have been deemed necessary to date, the most prudent condition for women intending to become pregnant is not to smoke and not to use NRT. As for men, it is known that smoking can cause adverse effects on male fertility, but there is no evidence that men need special contraceptive measures during NRT treatment. Pregnancy Smoking during pregnancy is associated with risks such as intrauterine growth retardation, premature birth or stillbirth. Smoking cessation is the only truly effective intervention to improve the health of the pregnant smoker and the baby. The earlier abstinence is achieved, the better the outcomes. Nicotine is transmitted to the fetus, with consequences on the respiratory movements and circulation of the latter. The effect on circulation is dose-dependent. Consequently, pregnant smokers should always be advised to stop smoking completely without resorting to nicotine replacement therapy. The risk of continued smoking may pose greater risks to the fetus than the use of nicotine replacement products in a supervised tobacco cessation programme. Use of Nicorettequick by pregnant smokers should only be undertaken on the advice of a healthcare professional. Breastfeeding Nicotine passes freely into breast milk in quantities that may be of benefit to the baby, even at therapeutic doses. Consequently, Nicorettequick should not be taken during breastfeeding. If smoking cessation is not possible, use of Nicorettequick by breastfeeding smokers should only be undertaken on the advice of a healthcare professional. Women should take the product immediately after breastfeeding and wait as long as possible (2 hours is recommended) before the next feed. Fertility Smoking increases the risk of infertility in women and men. In vitro studies have shown that nicotine can negatively affect the quality of human sperm. In rats, reduced fertility and impaired sperm quality have been demonstrated.
DRIVING AND USE OF MACHINERY
Taking NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses before driving or using machines - Does NicoretteQuick 1mg/spray 150 doses affect driving or using machines?
Nicorettequick has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.